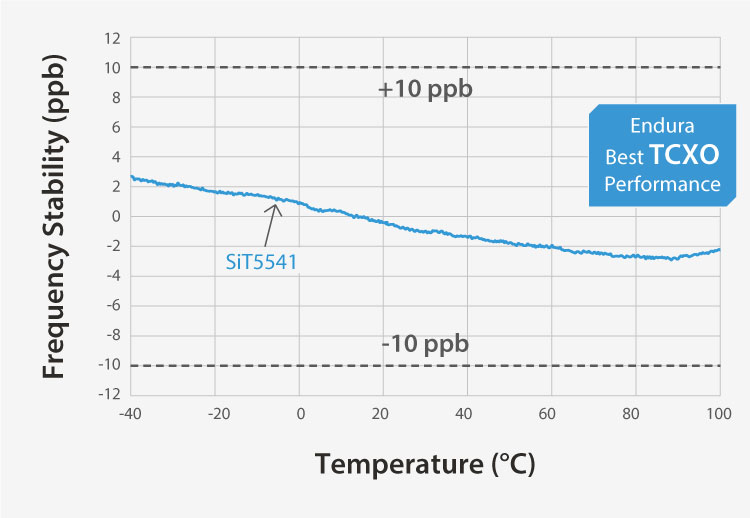
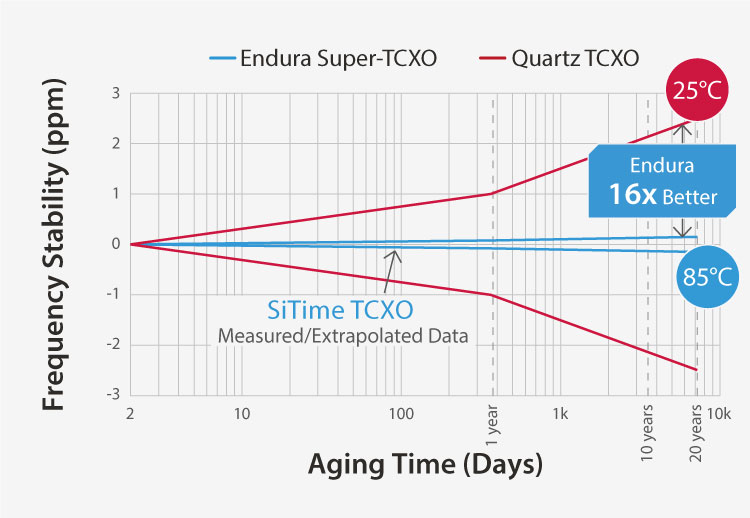
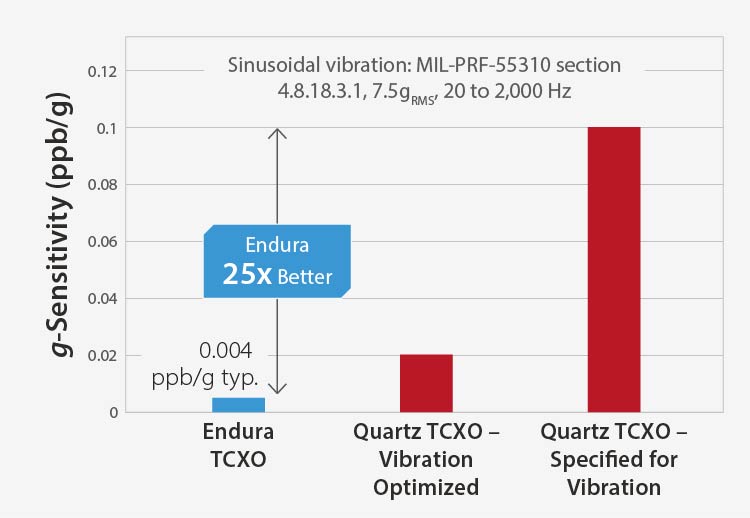
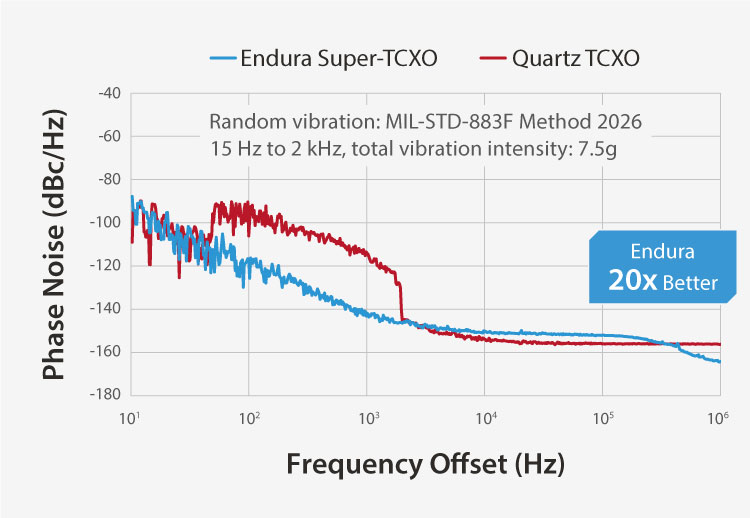
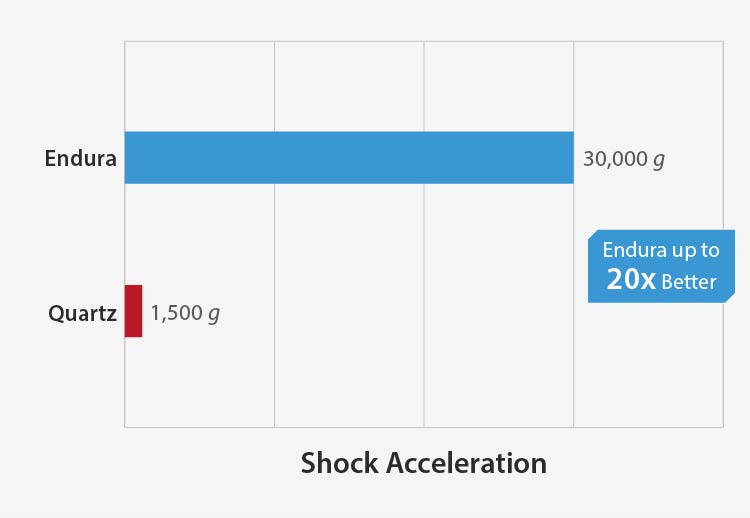
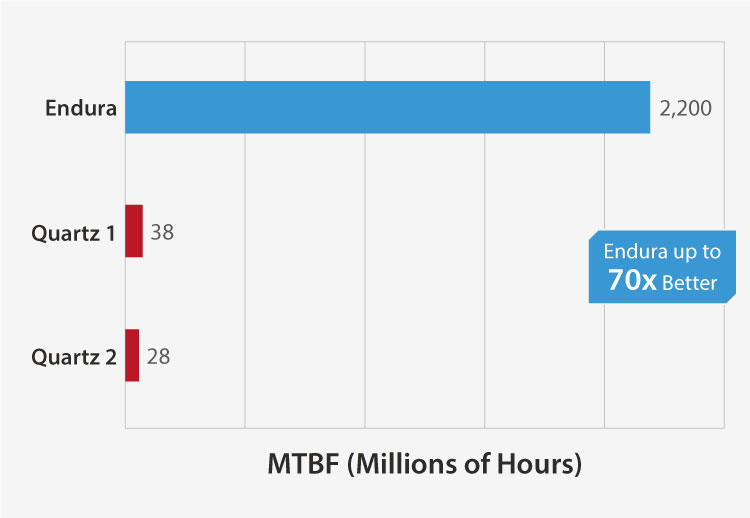
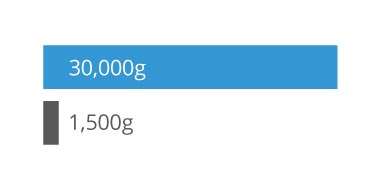
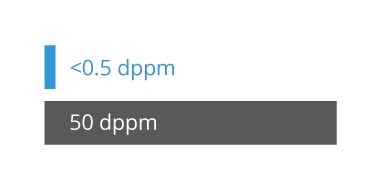
Endura MEMS Timing Solutions for LEO SatCom
| Devices | Key Features | Key Values |
|---|---|---|
|
Super-TCXO
SiT5146 1 to 60 MHz
SiT5147 60 to 220 MHz
|
|
Reference clock for uplink/downlink comms |
|
Differential XO
SiT9346 1 to 220 MHz
SiT9347 220 to 725 MHz
|
|
DSP, FPGA & processor clocking |
|
LVCMOS XO
SiT8944 1 to 110 MHz
SiT8945 115 to 137 MHz
|
|
DSP, FPGA & processor clocking |