Video Production Facilities
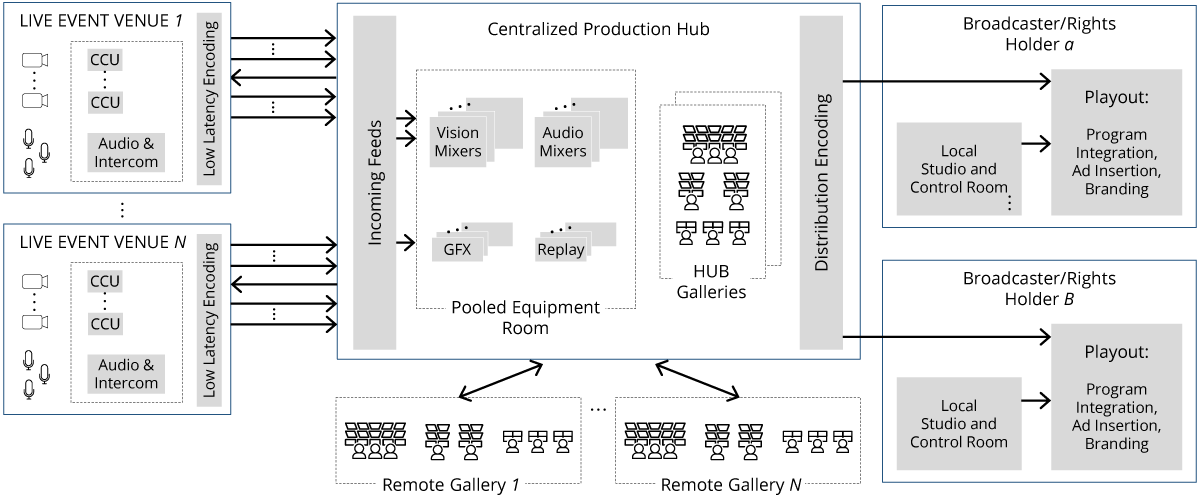
Video Production has evolved from an on-site production facility to remote production and finally to a centralized production facility. While on-site and remote had their advantages, the production companies now can accomplish more with a centralized facility.
Use cases of each type of facility are:
- On-Site: All production equipment and manpower is at venue (concert)
- Remote: Equipment and manpower is at a single location (Olympics)
- Centralized: Single facility housing arrays of equipment, manpower is remote (multiple concerts)
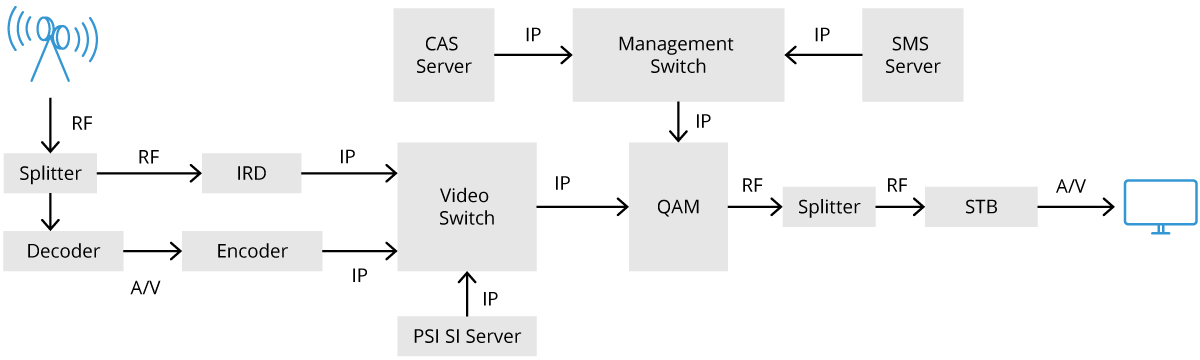
Video transmission has also evolved from conventional cable and satellite to streaming. Over The Top (OTT) is the terminology used for streaming. While conventional cable or IPTV networks rely on QAM and DSLAM equipment to deliver content to end users, OTT uses the cloud and related equipment such as mezzanine encoders, bitrate transcoders. and edge servers to deliver its content.
Applications
- Film / broadcast editing
- Live performances
- Educational events / conferences
- Event broadcasting
Video Production Evolution
A typical broadcast network uses many types of transmission equipment. Each type of equipment requires multiple timing components, such as single-ended clocks for general-purpose clocking, differential low-jitter clocks for Serdes clocking, and potentially synchronization devices for IEEE 1588 or AVB/TSN.
Conventional Video Processing